How to Make the Best Cold Process Soap: Super Moisturizing and High Lather
This cold-process shower soap recipe is the best ever. It makes a moisturizing yet cleansing bar with tons of lather. Please read below the recipe for tips on substations, safety, and storage, as well as step-by-step photos. If you’re brand new to soapmaking, there’s a lot to learn! You’ll want to watch the video and read the whole post before you start.
The Best Cold Process Soap Recipe

Equipment
- Safety equipment (gloves, goggles, apron)
Ingredients
- 11 ounces coconut oil
- 9 ounces olive oil
- 9 ounces palm oil
- 2 ounces sweet almond oil
- 4 ounces castor oil
- 4 ounces avocado oil
- 2 ounces mango butter
- 5.83 ounces lye
- 10-15 ounces water
- 3 tablespoons fragrance oil for a strong scent, vary this to your preferences
- 2 teaspoons sodium lactate optional, for a harder bar
- colorant or mica optional
Save This Recipe
You'll join my email list which you will love. And if you don't, unsubscribe in one click. ❤️
Instructions
- Make lye water. Using a digital scale, measure out the lye and water in separate glass containers. Combine them by adding the lye to the water. (Remember: snow floats on the lake.). Stir until the lye dissolves. The temperature will shoot up. Place this in a safe place to cool.

- Melt oils and butters. While the lye solution is cooling, measure out the oils and butters and combine them in a large stainless pot. Melt them over low heat and heat them up to 130-140 degrees. Set them aside to cool.

- Let cool. After 2 hours, check the temperature of both solutions. They should be around 110 degrees. (A range of 100-120 is fine.). If not, allow them to cool longer.
- Prep for mixing. Prepare your mold and measure out any fragrance or color you will be adding. (For best blending of colors, mix some color into a few drops of melted oils.). If using sodium lactate, add it to the lye water at this time.
- Blend to trace. Pour the water and lye solution into the pot with the melted oils. Blend with a stick blender until thin trace is reached. The soap batter will noticeable thicken and a trail of soap will sit on top of the liquid rather than immediately sinking in. (This will take about 1 minute.). Add the color and fragrance and stir by hand.

- Pour in mold. Immediately pour the soap batter into the mold. Place in a turned-off oven or wrap with blankets to insulate the soap.

- Cut bars and let cure. After 24 hours of curing, unmold and cut into bars. The bars may seem slightly soft but will harden considerably during the curing process. Allow to cure at least 3 weeks in a well-ventilated place.

Video
Notes
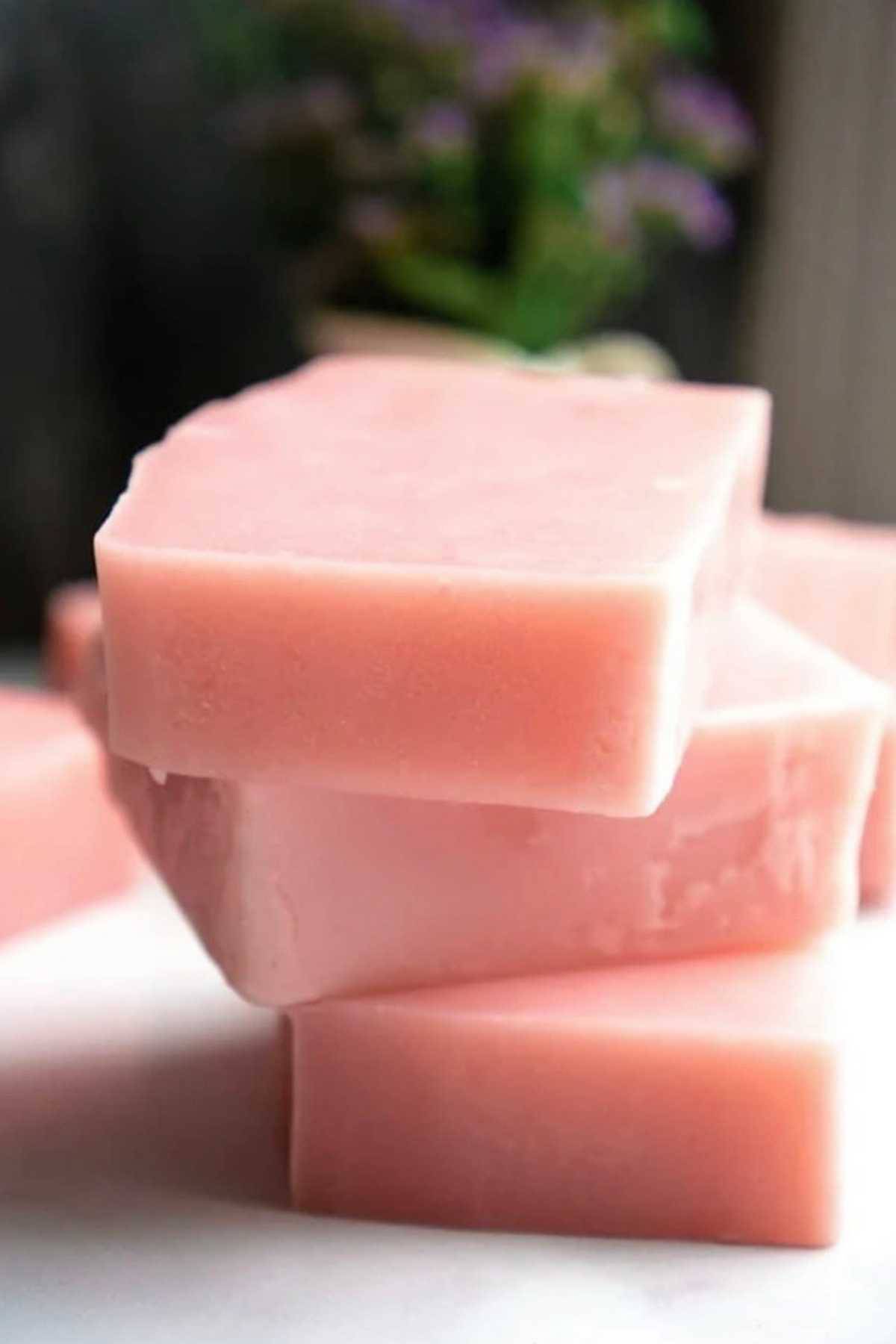

Ingredient Substitutions and Notes

- Coconut Oil: A staple in soap making, coconut oil provides a rich lather and hardness to the soap. It is highly cleansing and can strip away excess oil, making it ideal for oily skin types.
- Olive Oil: Known for its moisturizing properties, olive oil makes the soap smoother and less drying. It’s great for sensitive skin and contributes to the soap’s gentle cleansing ability.
- Palm Oil: Adds hardness to your soap bars, helping them maintain shape and last longer. It also contributes to lather quality, though it’s important to source sustainably due to environmental concerns.
- Sweet Almond Oil: This oil is excellent for its conditioning properties, adding softness and an elegant feel to the soap. It’s suitable for all skin types, especially dry skin.
- Castor Oil: A unique ingredient that boosts lather, making your soap rich and creamy. It’s also hydrating and helps draw moisture to the skin.
- Avocado Oil: Loaded with vitamins and minerals, avocado oil enhances the moisturizing power of your soap. It’s particularly good for dry and sensitive skin.
- Mango Butter: Provides a conditioning and moisturizing effect, making the soap more luxurious. Mango butter is rich in antioxidants and can help to soothe and soften the skin.
- Lye (Sodium Hydroxide): Essential for saponification, the chemical reaction that creates soap. Lye must be handled with care, but it is completely safe once the soap has cured.
- Water: Acts as a solvent for the lye and helps to control the saponification process. Distilled water is best to prevent any impurities from affecting the soap.
- Fragrance Oil: Adds a personal touch to your soap with your favorite scents. Quality fragrance oils are designed to be skin-safe and can significantly influence the sensory experience of using your soap.
- Sodium Lactate (optional): A salt solution that makes the soap bar harder and easier to unmold. While optional, it’s beneficial for achieving a smoother finish.
- Colorant or Mica (optional): These additives bring vibrant colors to your soap, enhancing its visual appeal. They can be used to achieve a wide range of artistic effects, like swirls or layers.
Storage Instructions
Once fully cured, homemade soap should be stored in a dry, well-ventilated spot. I like to put it in shoe boxes in the closet with layers of newspaper in between the bars.
While it is in use, use a soap saver to keep your bar dry. It will last much longer.
Common Issues and Fixes
A 10-inch silicone mold. It’s my favorite for most soaps.
If your soap is too soft, it might need more time to cure. Adding sodium lactate or using oils with higher stearic acid content can also help create a harder bar.
It is a pink mica from Nurture Soap. You can find it here.
Yes, absolutely. I’d recommend using sodium lactate since it can be a bit soft when unmolding it.
This is a 100% personal preference (except for the fact that florals are more difficult to work with). My personal favorites are Comfort and Joy from Nurture Soap and Mango Mango from Brambleberry.
Yes! I used to swirl it all the time before I got too lazy.
You sure can. You’ll need the following percentages:
Coconut Oil: 26.83%
Mango Butter: 4.88%
Olive Oil: 21.95%
Palm Oil: 21.95%
Sweet Almond Oil: 4.88%
Enter them into a soap calculator with the desired size of your batch and it will give you the correct amounts.
The gel phase is a part of the saponification process where the soap heats up and becomes translucent. This can help create a smoother, more uniform bar.
Yes, essential oils can be used as a natural alternative to fragrance oils. Just be sure to use skin-safe essential oils and follow recommended usage rates.
This recipe is a great way to start, but if it’s your first time, you might want to try a more basic recipe with fewer oils. Cold process soapmaking can be complex, so starting simple is a good idea.
Distilled water is free from impurities that can affect the chemical reaction during the saponification process. Using distilled water ensures a more consistent result.
More Great Cold Process Soap Recipes:
- Mix-ins are fun! Try this gardener’s soap recipe.
- You can make your own bar dish soap.
- If you’re looking for something palm-free, try my grapefruit soap bar.
As you continue soap-making journey, remember the importance of safety, stay patient and careful, and enjoy of crafting something with your own hands.
Love,







Excellent indeed. I will definitely try it.
Hey Hillary, thank you so much! I’m so glad you liked it. I hope you have fun making the soap, it’s such a rewarding process! Let me know how it turns out or if you have any questions along the way.
Hi, I was wondering what other oil or butter I can substitute for palm oil.
I have made soap before using your recipe and it was great but my palm oil is out of date now.
Hey Kate,
So glad you enjoyed the recipe! If you’re out of palm oil, you can substitute it with lard, shea butter, or cocoa butter. Lard is the closest match, but shea or cocoa butter will work too—they might just make the bar a little harder. Be sure to run the new recipe through a soap calculator to adjust the lye amount. Let me know how it turns out!:)
i made this years ago. it s the best soap i ever made.
Hi Katie,
I’ve been making this recipe for years, and my family really enjoys. Olive oil is getting so expensive, and I understand lard can be a good substitute. My question is can you use the same amount of lard to replace the olive oil, or do you have to change the amount?
Thank you for a wonderful recipe!
Blessings,
Michelle
Hi Katie,
We’ve been making this soap regularly for years and we love it. I’m sure you’ve noticed the price of olive oil going up, and I understand that lard is a good substitute for olive. Can you use 9 ounces of lard in place of the olive oil in this recipe or do you have to change the amount? Thanks for your help and for the wonderful recipe.
Blessings,
Michelle
hey Michelle! it should be a good substitute in terms of keeping the same properties, BUT run it through a lye calculator to be sure the amount of lye doesn’t change. BTW… you can buy olive oil specifically for soap that is NOT food grade and is much cheaper.
Wonderful recipe with some wriggle room to get creative. Easy to follow instructions.
Could you substitute goat milk for the water equally? Thanks.
yes that is just fine 🙂
I followed everything to a t but I only blended for about 12 seconds and it started to harden I made individual bars and by the last bar you had to push it into the form. 24 hours later there were large spots of oil on top and as I removed them from the mold my fingers stung from the lye. I can’t figure out what went wrong the temperature was 112
hi jamie, 12 seconds is definitely not enough time for everythig to come to trace. you may have used a fragrance that made the soap difficult to work with and hardened before it was really blended.
Absolutely wonderful!! Was so pleased with the results! Thank you for sharing.
I’m curious about your water ingredient as 10-15 ounces. don’t you need an exact amount? thanks!
hey stef! you don’t need an exact amount, water is the ONE thing that’s flexible in a soap recipe. less water will give ou a bar that cures/. drys out faster, but also traces quickly, giving you less time to pour, etc. its up to you :). i use around 12 🙂
My soap turned out yellow but I need a batch of white. What should I do?
Add titanium dioxide as your colorant 🙂
This recipe looks OK, however, it is a common misconception that the “cleansing” number on a soap calculator tells how well the soap cleans. All soap cleans…the cleansing number actually tells you how much oil is stripped from your skin. The lower the cleansing number, the more moisturizing the soap will be. I always keep my cleansing number below 10, and prefer it to be <3.
Just food for thought 🙂
Hi there I’m new to soap making and I was wondering how to incorporate duck fat into this recipe. Any advice is greatly appreciated
hey kim, i’ve never worked with it but if you look up tallow soap making it might point you in the right direction. oncce you get a sense of the basic process there, I have a post on how to make your own soap recipes and you can use a lye calculator to get exact measurements. hope this helps 🙂